What is Cloud Orchestration?
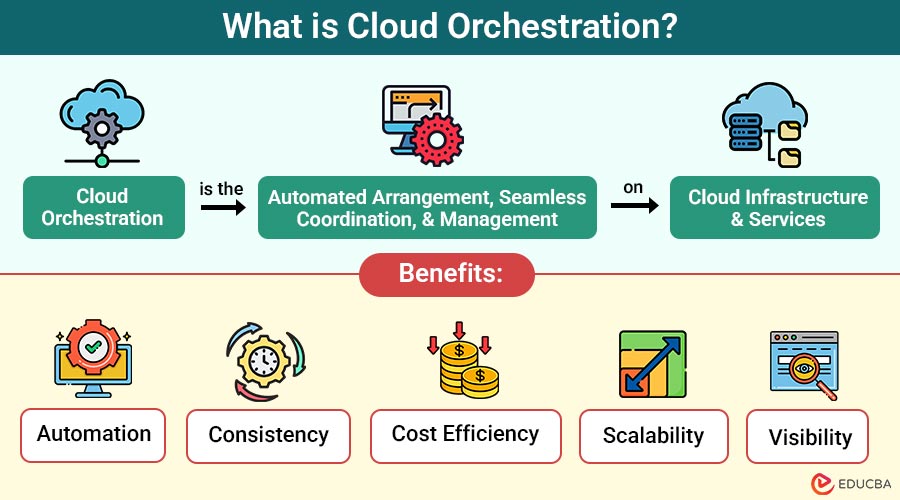
Cloud Orchestration is the automated arrangement, seamless coordination, and management of cloud infrastructure and services. It involves integrating various automated tasks into workflows that perform complex processes, like deploying applications, provisioning servers, scaling resources, or managing storage.
Think of orchestration like a movie director. Each cloud resource (compute, storage, network) is an actor. Orchestration ensures they perform their roles at the right time and in the right order without requiring manual supervision.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Cloud orchestration streamlines the management of dynamic infrastructure by automating the coordination of services and resources across the entire infrastructure.
- It empowers teams to deliver scalable and reliable environments without requiring deep involvement in operational processes.
- Orchestration bridges the gap between complex cloud operations and streamlined, consistent application performance.
- To ensure orchestration aligns with corporate objectives and settings, selecting the appropriate tool is essential.
Why is Cloud Orchestration Important?
Without orchestration, managing cloud infrastructure involves several manual steps:
1. Provisioning Virtual Machines
Provisioning VMs manually involves allocating resources, selecting images, and launching instances—this process is repetitive, error-prone, and inefficient at scale.
2. Configuring Networks
Manual network configuration involves setting up IP addresses, subnets, firewalls, and routes—a complex, time-consuming, and challenging task to maintain across different environments.
3. Managing Storage and Databases
Handling storage and databases manually involves provisioning, setting access, managing backups, and replication, which can lead to errors, data loss, or inconsistent performance.
4. Ensuring Services Run in the Correct Order
Starting services in the proper order manually can cause dependency failures and delays—automation ensures that components initialize and function in the correct sequence.
5. Handling Failures or Changes
Manual failure response and configuration updates are slow and risky; cloud orchestration enables automated recovery, scaling, and consistency across environments during changes.
How does Cloud Orchestration Work?
Cloud Orchestration tools use predefined templates, scripts, or workflows to automate the deployment and management of cloud resources.
Key Components:
- Blueprint or Template: A predefined configuration (e.g., YAML or JSON file) that describes what to deploy and how.
- Workflow Engine: Executes steps in sequence (e.g., first create VM, then configure software, then connect to the network).
- APIs and Integrations: Orchestration tools use APIs to communicate with cloud services (e.g., AWS, Azure, Google Cloud).
- Monitoring and Feedback: Orchestration tools monitor operations and make necessary adjustments in response to their success or failure.
Typical Workflow Example:
User request: Deploy a 3-tier application
- Step 1: Provision servers (Web, App, DB)
- Step 2: Configure load balancer and firewall
- Step 3: Install software and databases
- Step 4: Set up auto-scaling and monitoring
- Step 5: Confirm deployment status
All of this happens automatically with minimal human intervention.
Benefits of Cloud Orchestration
Cloud orchestration offers several benefits that streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve overall efficiency:
1. Automation
Reduces repetitive manual tasks by automating workflows, streamlining operations, and enhancing efficiency across infrastructure and application deployment processes.
2. Consistency
Ensures consistent and dependable deployments by using standard settings, which helps reduce mistakes and keeps performance the same across all cloud environments.
3. Cost Efficiency
Maximizes resource usage by dynamically allocating workloads, reducing idle infrastructure, and helping businesses cut operational costs without sacrificing performance.
4. Scalability
Automatically adjusts resources to meet workload demands, ensuring optimal performance under load spikes while optimizing costs during periods of low usage.
5. Visibility
Provides centralized monitoring and control, offering real-time insights into infrastructure, workflows, and performance for better decision-making and troubleshooting.
Popular Cloud Orchestration Tools
Several tools help organizations implement orchestration, including:
1. AWS CloudFormation
- Automates infrastructure as code (IaC) on AWS
- Uses JSON/YAML templates
- Integrates with other AWS services
2. Azure Resource Manager
- Orchestrates deployments in Microsoft Azure
- Uses templates for consistency
- Manages dependencies and rollbacks
3. Google Cloud Deployment Manager
- Manages resources on Google Cloud
- Uses YAML-based configuration files
4. Terraform
- Platform-agnostic IaC tool
- Works across multiple cloud providers
- Highly flexible and scalable
5. Kubernetes
- Orchestrates containerized applications
- Manages pods, scaling, and service discovery
- Ideal for microservices and DevOps pipelines
6. Ansible
- Uses YAML playbooks
- Great for configuration management and orchestration
- Works across bare metal, cloud, and hybrid environments
Real-World Use Cases
Cloud orchestration is widely applied across industries to simplify operations, enhance agility, and improve service reliability. Here are some common scenarios:
1. Multi-Cloud Deployments
Companies use orchestration tools to manage resources across AWS, Azure, and GCP seamlessly.
2. DevOps and CI/CD Pipelines
Orchestration automates code deployment, testing, and rollback in continuous integration and delivery setups.
3. Disaster Recovery
In case of failure, orchestration can automatically spin up backup environments to ensure business continuity.
4. Auto-Scaling Applications
Apps hosted in the cloud can scale up or down automatically based on demand using orchestrated workflows.
5. SaaS Provisioning
Software providers utilize orchestration to onboard new users by instantly provisioning storage, databases, and services.
Challenges and Considerations
While Cloud Orchestration is powerful, there are challenges:
1. Complex Setup
Cloud orchestration can be complex. To handle it well, begin with a small setup, test it carefully, and slowly expand as your team becomes more skilled and confident.
2. Learning Curve
New users may find it hard to learn at first. To help them get started faster, use ready-made templates, follow official guides, and provide training materials to make learning easier and tool usage more effective.
3. Tool Compatibility
Not all orchestration tools work seamlessly with every cloud service. Select orchestration tools specifically designed for your cloud provider to ensure optimal performance and support.
4. Security Risks
If roles or secrets are not handled properly, it can lead to security issues. To stay safe, use encrypted passwords or keys, give users only the access they need, and set clear role-based permissions for everyone.
5. Debugging Errors
Orchestration workflows can fail silently. Mitigate this by using robust logging and monitoring tools to quickly identify, analyze, and resolve errors within automated processes.
Best Practices for Cloud Orchestration
To maximize efficiency, reliability, and scalability, organizations should follow these proven cloud orchestration practices:
1. Use Infrastructure as Code
Handle your infrastructure like you handle application code. Save setup files in version control tools to keep track of changes, work better as a team, and make cloud deployments easier and more consistent.
2. Test Before Deploying
Always test your orchestration workflows in a staging environment before using them in the live system. This helps catch problems early, reduces risks, and makes sure everything runs smoothly when deployed to production.
3. Modular Template
Break orchestration templates into smaller, reusable modules. This promotes cleaner organization, simplifies maintenance, and encourages consistent reuse across multiple services, teams, or cloud environments.
4. Implement Logging
Enable detailed logging for every orchestration process. Logs help you trace workflow issues, pinpoint failures, and speed up debugging, ultimately improving operational reliability and transparency.
5. Monitor Resources
Use live dashboards to keep an eye on what’s happening in your cloud system. This helps you quickly spot any problems, make better use of resources, and keep everything running smoothly and reliably.
Final Thoughts
Cloud Orchestration is the backbone of modern cloud infrastructure management. It automates complex workflows, ensures consistency, and enables businesses to operate efficiently at scale. Whether you are managing one cloud or many, orchestration helps you do it faster, safer, and smarter. Businesses may fully utilize cloud computing without the turmoil by implementing the appropriate tools and adhering to best practices.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is cloud orchestration the same as DevOps?
Answer: Not exactly. DevOps is a cultural and operational approach, while orchestration is a technical method used within DevOps to automate workflows.
Q2. Do I need coding skills for orchestration?
Answer: Basic scripting knowledge helps. Many tools use YAML or JSON, which are human-readable formats.
Q3. How does orchestration help with security?
Answer: It applies security policies consistently and can automatically configure firewalls, access controls, and encryption.
Q4. What is the difference between orchestration and scheduling?
Answer: Scheduling runs tasks at specific times. Orchestration manages how and when various tasks run together.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Cloud Orchestration” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.


